In order to notice pathological changes in the condition of the nails and skin of the feet in time and begin treatment as quickly as possible, it is important to know what nail plate fungus looks like. The sooner measures are taken to eliminate the disease, the greater the likelihood that it will be possible to prevent the destruction of the nail plate and restore its normal appearance. Find out how the fungus manifests itself at different stages and what are the characteristic features of the course of this disease.
What does onychomycosis look like?
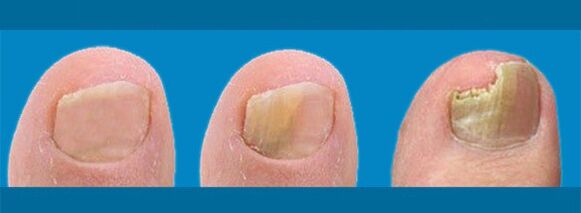
To understand that the nail plates have been infected with a fungal infection (onychomycosis), you need to know what healthy nails look like. In normal condition, nails are smooth, horny plates of a pale pink color, smooth, without dents, bumps or delaminations. Healthy nails are strong and elastic, not thickened. But a change in their appearance can signal many pathological processes in the body, so it is necessary to identify specific symptoms inherent in onychomycosis. They may vary depending on the form of the disease.
- Normotrophic.This is the initial stage of nail fungus. The horny plates change color, yellowish and white spots and stripes appear on them, as well as an unpleasant odor. This is the initial stage of the disease, so the nail retains its normal thickness and relatively healthy appearance. This stage begins to appear at the end of the incubation period.
- Hypertrophic:the color changes even more, the plates begin to thicken, and the shine disappears. A change in shape and partial destruction of the plate along the edges may be observed.
- Atrophic:the affected nail is separated from the nail bed.
Another classification also depends on what nail fungus looks like. It involves dividing the infection into several types depending on which part of the nail is affected by the fungus:
- Distal.There is delamination and yellowing of the edge of the plate, keratinization of the nail bed. In some cases, the nail may be completely affected, and its root (matrix) may also become infected. Thinning of the plate may occur.
- Surface.The fungus affects the upper part of the horny plate, causing the appearance of white stripes and spots that turn yellow and increase in size over time. They can be easily removed by scraping. The plate has a loose structure. This variety is specific: this is how toenail fungus manifests itself.
- Proximal.Fungus occurs under the nail, causing damage to the matrix and tissues surrounding the plate. Cuticle rejection may occur. Deep grooves and irregularities appear on the nails.
- Total. The nails acquire a gray-yellow tint, become very thick and peel. The plate undergoes complete or partial destruction.
Foot skin fungus
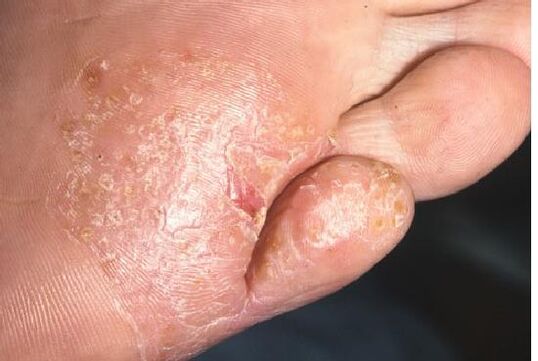
Often, the fungus on the toenails spreads to the skin of the feet. What does fungus look like on the skin of the feet?
In the first stages, infection manifests itself in the form of redness and swelling of the skin, and the appearance of small cracks.
Most often, changes can be noticed between the toes and on the heels.
The next symptom of mycosis of the feet is the appearance of spots on the skin, which soon begin to itch and peel. Over time, the size of these spots increases, involving an increasingly larger area of skin in the fungal process. There is an unpleasant odor from the feet, even if you do not wear shoes. If treated incorrectly or untimely, foot fungus can develop into an extensive form, in which deep cracks form at the base of the toes and between them, on the arch of the foot and on the heels. In addition, this stage is characterized by severe separation of the skin.
Diagnosis of fungal nail infections
Any person who is far from medicine can suspect a nail or foot fungal infection if he has at least a faint understanding of this disease. However, only a qualified specialist can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment based on an external examination, a survey of the patient, and data from studies of the affected nail under a microscope. In this case, you need to contact a dermatologist.
To determine whether a patient actually has a fungal infection, a scraping is taken from the affected nail in the laboratory and, after placing the material in an alkaline environment, it is examined for the presence of fungal mycelium under a microscope. If such a specific structure is discovered, the diagnosis will be absolutely confirmed. Additional studies may be prescribed to determine the specific type of fungus; this is necessary to select the most effective drugs against infection.
Nail fungus not only spoils the appearance of the hands and feet, but can also lead to unpleasant consequences, including complete loss of the nail plates and the penetration of a fungal infection into the body. In addition, onychomycosis and foot fungus are contagious diseases, so at the first symptoms you need to consult a doctor as soon as possible to protect your loved ones. The incubation period of the fungus can take several weeks, so the disease does not appear immediately. The sooner you seek help from a specialist and accurately diagnose the disease, the faster the treatment will take place and the less money you will have to spend on expensive medications with antifungal action.















